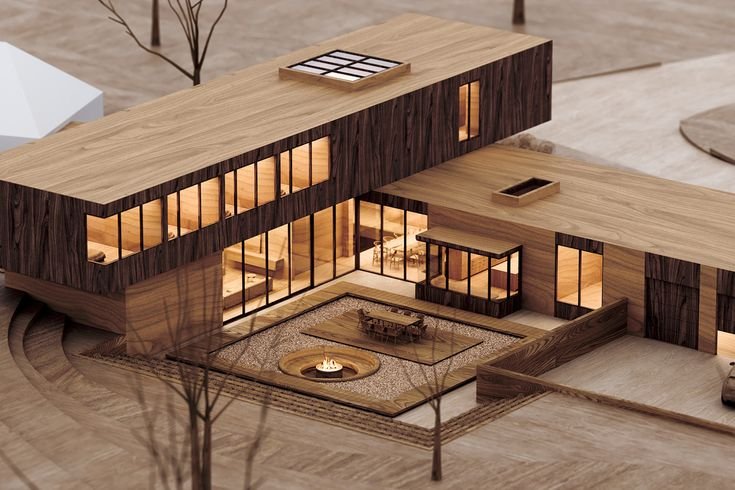
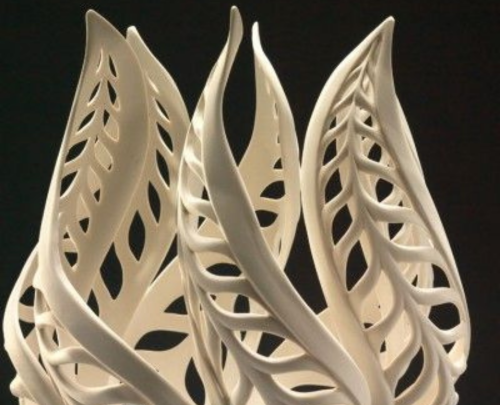
In the dynamic landscape of contemporary design, 3D printing has emerged as a revolutionary tool, reshaping industries and pushing the boundaries of traditional design paradigms. The realm of interior design, in particular, has witnessed a profound transformation through the integration of 3D printing technologies. Designers are now equipped with a powerful arsenal, enabling them to translate imagination into tangible reality. For instance, intricately designed furniture pieces, such as avant-garde chairs with complex geometric patterns or uniquely shaped bookshelves, are brought to life with precision and detail that was once unimaginable. This bespoke approach not only caters to individual preferences but also allows for the seamless integration of these pieces into diverse spatial contexts.

Take, for example, the concept of personalized lighting fixtures. With 3D printing, designers can create intricate lampshades that cast captivating patterns of light, transforming a functional element into a work of art. Homeowners can actively engage in the design process, choosing patterns, materials, and sizes that resonate with their aesthetic. This collaborative approach between designers and homeowners is fostering a new era of co-creation, where the result is not just a piece of furniture but a reflection of individuality and style.

Moreover, the flexibility afforded by 3D printing extends beyond aesthetics to practical considerations. Designers can tailor furniture and fixtures to specific spatial requirements, optimizing functionality without compromising on design. Think of a custom-designed wall-mounted shelf perfectly fitting an awkward nook or a desk seamlessly integrated into a compact home office space. 3D printing, in this context, is not just a technological innovation but a facilitator of design thinking that places the user’s needs and preferences at the forefront, forging a symbiotic relationship between form and function in the realm of interior design.

Venturing beyond the confines of interior design, 3D printing has emerged as a transformative force in the expansive field of architecture. Architects are now harnessing the capabilities of this cutting-edge technology to propel their visionary designs from conceptualization to tangible reality. The integration of 3D printing in architecture marks a significant leap forward, offering architects unprecedented precision and efficiency in the realization of their projects.
In the realm of architectural modelling, 3D printing has revolutionized the way architects bring their concepts to life. Elaborate and intricate models, once laboriously crafted by hand, are now meticulously reproduced with unparalleled accuracy using 3D printing techniques. This technological leap not only saves valuable time but also allows architects to iterate rapidly, refining their designs in response to evolving ideas and client feedback. The result is a more dynamic and responsive design process that brings a level of detail and intricacy to architectural models that were previously impractical.

Moreover, 3D printing has become a linchpin in the construction phase of architectural projects. The technology streamlines the construction process by enabling the creation of prefabricated components with intricate geometries that would be challenging or impossible to achieve through traditional methods. This not only enhances the structural integrity of buildings but also significantly reduces waste, contributing to a more sustainable approach to construction. Imagine the creation of complex facades or structural elements that seamlessly fit together like a puzzle, all made possible through the precision and adaptability of 3D printing in architecture.
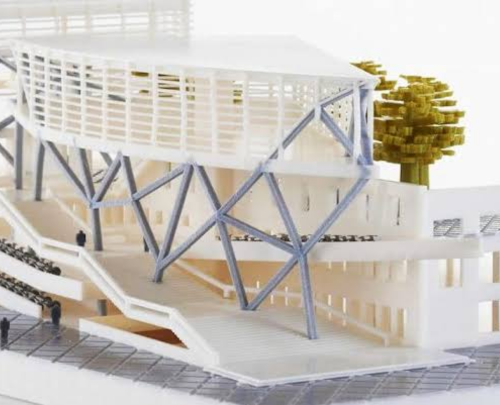

At the forefront of technological innovation, 3D printing emerges as a champion in the quest for sustainable practices. Its most compelling feature lies in the meticulous precision with which it utilizes materials, minimizing waste and significantly reducing the environmental impact traditionally associated with manufacturing. By enabling more efficient use of resources, 3D printing takes a giant stride towards environmental stewardship.

The shift towards a circular economy, characterized by the continual use and recycling of materials, is expedited by the eco-friendly nature of 3D printing. The technology facilitates the creation of durable and recyclable products, marking a substantial leap towards a greener and more sustainable future. As 3D printing becomes increasingly integrated into manufacturing processes, its role in fostering environmental responsibility becomes a beacon of hope in an era where sustainability is paramount.